The function of the charging station is similar to that of a gasoline dispenser inside a gas post, which can reach the ground or wall. It gets in place in public buildings (public buildings, shopping malls, public parking lots, etc.) and residential community parking lots or charging stations. It can charge various models of electric vehicles according to different voltage levels.
1. Charging Principle of Charging Station
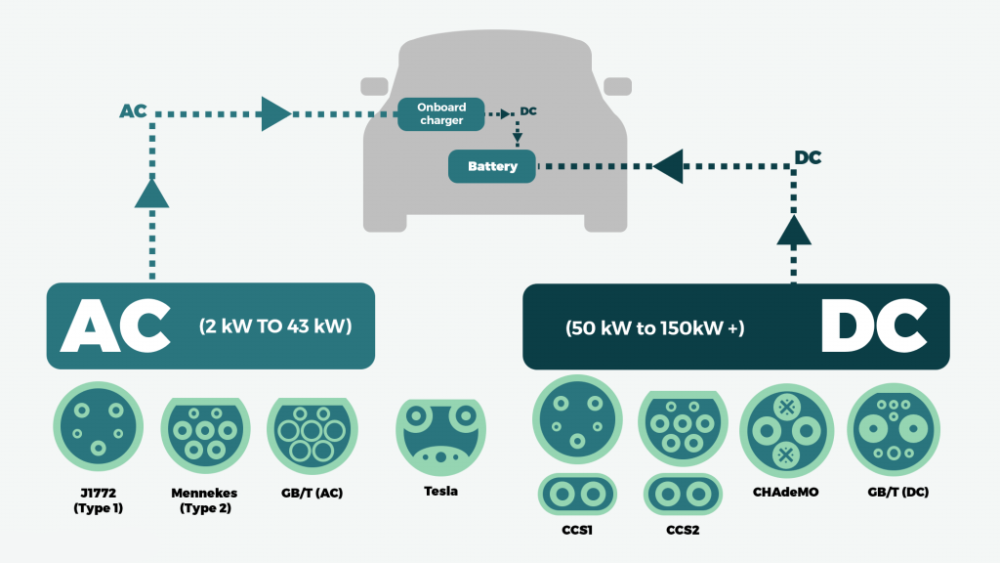
AC charging stations are also known as AC power supply units. It sits on the ground and connects to the AC grid. Using a special charging interface, it uses conduction to provide AC power to electric vehicles with onboard chargers. It has corresponding communication, billing, and safety protection functions. The AC charging station only provides power output, no charging function, and needs to work with a vehicle charger to charge the electric vehicle.
After the electric vehicle battery with discharged, DC power passes through the battery in the opposite direction of the discharge current. This process is known as battery charging. When the battery is in charge, the positive terminal is on the positive side of the power supply. The battery’s negative terminal is in connection with the negative terminal of the power supply. The voltage of the charging power supply must be higher than the total electric potential of the battery.
The DC comes with variable voltage rectification, and the output is the high voltage DC that the battery can use directly. Because most of them are many parallel connections, they can output high currents. The AC charging station is essentially a socket with control, and the output is AC power. It requires the vehicle charger to carry out its voltage rectification. Limited by the power of the vehicle charger, the general power is small, 3.3 and 7kw mostly.
2. AC Charging Station Design Requirements
- It can provide AC220V/7kw power supply capacity.
- Protection functions include leakage, short circuit, over-voltage, under-voltage, over-current, etc. Ensure safe and reliable operation of the charging station.
- With the necessary human-machine interface for display, operation, etc.
- AC charging metering.
- Set the card swipe interface, supporting RFID card, IC card, and other common card swipe methods.
- It has perfect safety protection control logic such as connection state judgment of charging interface and control guidance. (The power requirement of the AC charging station is input voltage: single-phase AC220V±10%, output frequency 50Hz±2%, the output is AC220V/7kw)
3. Charging Method of Charging Station
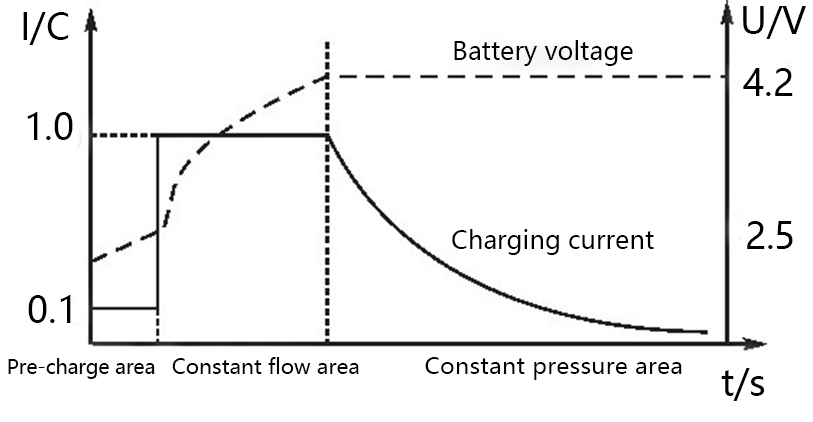
Constant Current Charging Method
The constant current charging method is a method of adjusting the output voltage of the charging device or changing the resistance in series with the battery. The charging current intensity is kept constant. The control method is simple, but the acceptable current capacity of the battery is gradually decreasing as the charging process proceeds.
By the late stage of charging, the charging current is mostly used for electrolysis of water, producing gas and making the outgassing too much. Therefore, the stage charging method is often to choose.
Constant Voltage Charging Method
The voltage of the charging power supply is constant for the entire charging time. The current gradually decreases as the battery terminal voltage gradually increases. The charging process is closer to the optimal charging curve than the constant current charging method.
With constant voltage fast charging, the charging current is high due to the low electric potential of the battery at the beginning of charging, and the current will gradually decrease as the charging progresses.
4. Difference Between DC Charging Station and AC Charging Station
DC electric vehicle charging station, commonly known as “fast charging”. It is a fixed installation outside the electric vehicle and connected to the AC grid. It is a power supply device that can provide DC power supply for non-vehicle electric vehicle power batteries.
The input voltage of the DC charging station adopts a three-phase four-wire AC 380V±15%, frequency 50Hz, and the output is adjustable DC power. It directly charges the power battery of electric vehicles. As the DC charging station adopts a three-phase four-wire power supply system, it can provide enough power, and the output voltage and current adjustment range is large, which can realize the requirement of fast charging.

AC electric vehicle charging post, commonly known as “slow charging”. It is a power supply unit outside of an electric vehicle that is set up to connect to the AC grid. AC power is to the onboard charger of the EV (i.e., the charger fixed to the EV). The AC charging station only provides power output and has no charging function. It must work with an onboard charger to charge the electric vehicle. It is equivalent to the role of a control power supply.

In short, AC charging stations need to charge with an onboard charger, while DC fast-charging stations do not need this equipment. There is a big difference in charging speed between the two. A pure electric car (normal battery capacity) takes 8 hours to make a full charge through an AC charging station after complete discharge, while it only takes 2 to 3 hours through a DC fast charging station. Equivalent to the role of a control power supply.


thanks, interesting read
The main difference between DC and AC charging stations lies in their charging principles and speed. AC charging stations provide power output and require an onboard charger in the electric vehicle to charge it, making them slower, taking around 8 hours for a full charge. On the other hand, DC fast-charging stations directly supply DC power to the EV’s power battery, eliminating the need for an onboard charger and significantly reducing charging time to 2-3 hours for a full charge. DC charging stations are known for their fast-charging capabilities, making them more suitable for quick recharges in public spaces or on the go.
interesting post