Energy storage technologies are technologies that store energy through devices or physical media for later utilization when needed. Energy storage technology can be categorized according to the storage medium, can be divided into mechanical energy storage, electrical energy storage, electrochemical energy storage, thermal energy storage and chemical energy storage.
This paper focuses on three of the main electrical energy storage technologies. They are pump energy storage, compressed air energy storage and electrochemical energy storage.
1. Pumped Storage
This is currently the most widely used large-scale power storage technology.
(1) Basic Principle
Pumps and turbines are set up between two reservoirs at different heights. At times of low power loads, electrically driven pumps are used to pump water from the lower reservoir to the higher reservoir. At peak loads, water is released from the high reservoirs to generate electricity through the turbine-generator units.
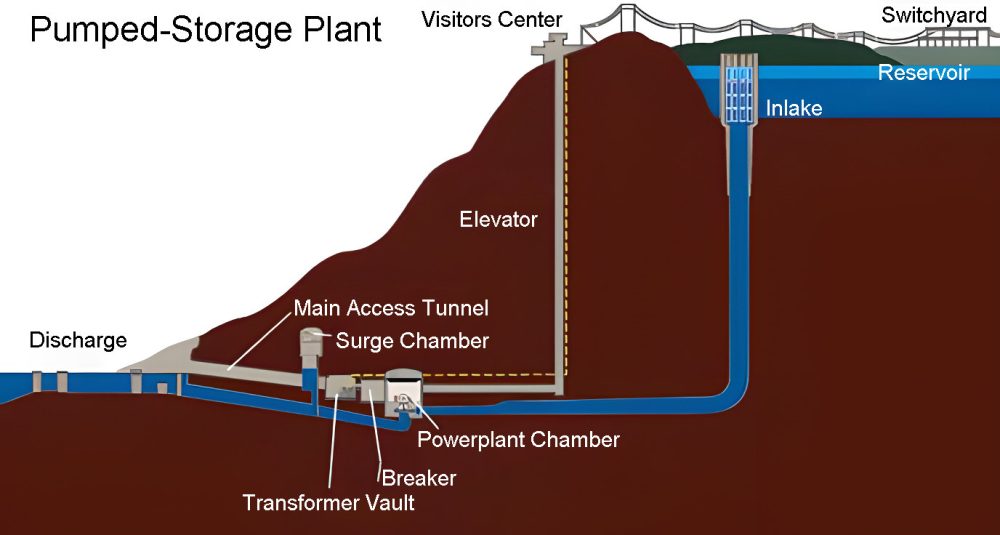
(2) Characteristics
- It belongs to large-scale, centralized energy storage, and the technology is quite mature, which can be used for energy management and peaking of the power grid.
- Efficiency is generally about 65%~75%, and can reach up to 80%~85%.
- Fast load response (10% load change takes 10 seconds), from full stop to full load generation in about 5 minutes, from full stop to full load pumping in about 1 minute.
- Has the ability of daily regulation, suitable for cooperation with nuclear power plants, large-scale wind power generation, ultra-large-scale solar photovoltaic power generation.
(3) Disadvantages
- Needs upper and lower pools.
- The choice of plant site depends on geographical conditions, which has certain difficulties and limitations.
- There is a certain distance from the load center, long distance transmission is required.
(4) Application
Currently, the world average for the share of pumped storage units in a country’s total installed capacity is about 3%. As of the end of 2019, the total capacity of energy storage units in the world was 184.6GW, of which pumped storage was 171.0GW, accounting for 92.63%.
2. Compressed Air Energy Storage
Compressed air is stored in cylinders or underground storage tanks to store the potential energy of compressed air. When electricity is needed, the compressed air is released to drive the turbine to generate electricity.
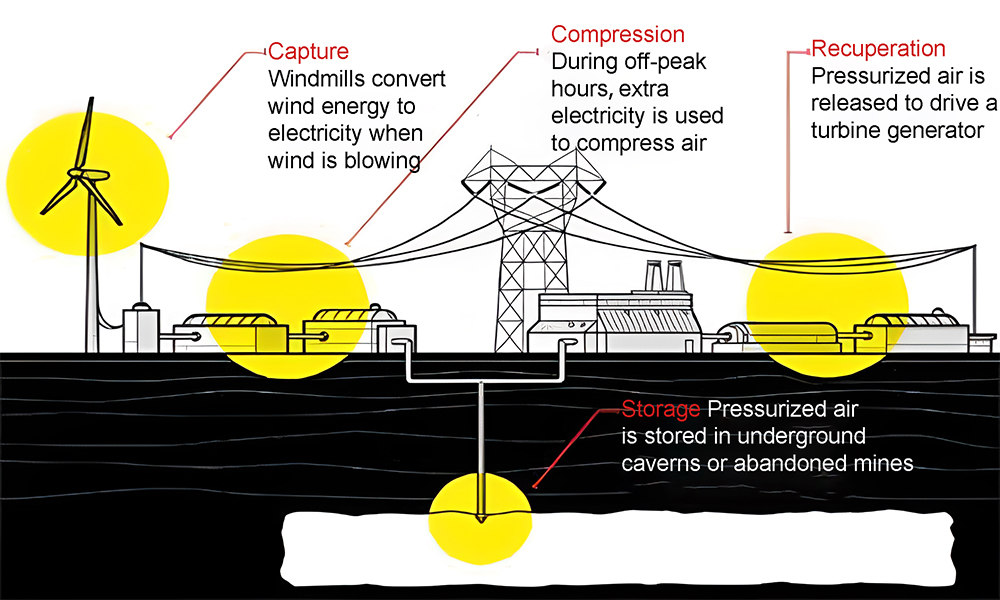
(1) Basic Principle
Compressed air energy storage using air as a carrier of energy. Large-scale compressed air energy storage using excess electricity will be compressed air and stored in an underground structure (such as underground caves). When needed, the compressed air is then mixed with natural gas and burned and expanded to power a gas turbine.
Currently there are various forms of compressed air energy storage systems. Which can be categorized according to the working medium, storage medium and heat source: conventional compressed air energy storage systems (which require fossil fuel combustion), compressed air energy storage systems with heat storage devices, and liquid-gas compression energy storage systems.
(2) Advantages
It has a peak shifting function and is suitable for use in large-scale wind farms. Because the mechanical work generated by wind energy can directly drive the compressor to rotate, reducing the intermediate conversion into electricity, thus improving efficiency.
(3) Disadvantages
Requires a large cavern to store compressed air, is closely related to geographical conditions, and is suitable for a very limited number of locations.
Requires a gas turbine and a certain amount of gas as fuel, and is suitable for energy management, load leveling, and peak shaving.
A non-adiabatic compressed air energy storage technology has been developed in the past. The heat released when the air is compressed is not stored and is dissipated through cooling. Instead, the compressed air needs to be reheated before entering the turbine. The efficiency of the whole process is therefore low, usually below 50%.
(4) The significance of compressed air energy storage power plant:
Air is the best choice for “energy multimedia”. It is a global trend to vigorously develop solar, wind, wave and nuclear energy, but supply and demand are often asynchronous and unbalanced. The only “energy multimedia” capable of converting, storing, and accessing all forms of energy is “air”. And it is the “best candidate” for this “role”.
Huge economic and social benefits calculated on the basis of one-third of the power generation capacity, can save four or five hundred million tons of coal per year. This is equivalent to the annual output of dozens of medium and large coal mines. And year after year, the economic and social benefits are huge, saving a lot of resources and promoting sustainable economic and social development.
3. Electrochemical Storage
Electrochemical storage mainly includes a variety of secondary batteries, lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries, sodium-sulfur batteries and liquid current batteries. Application of various batteries (mainly lithium-ion batteries) chemical storage principle to store electrical energy. When charging the electrical energy is converted into chemical energy of the battery, and when discharging the chemical energy is converted into electrical energy output.
In which lead-acid batteries and lithium batteries are more widely used.
3.1 Lead-acid Batteries
(1) Basic Principle
Lead-acid battery is one of the most widely used batteries in the world. Lead-acid batteries within the anode (PbO2) and cathode (Pb) immersed in the electrolyte (dilute sulfuric acid), between the two poles will produce a potential of 2V.
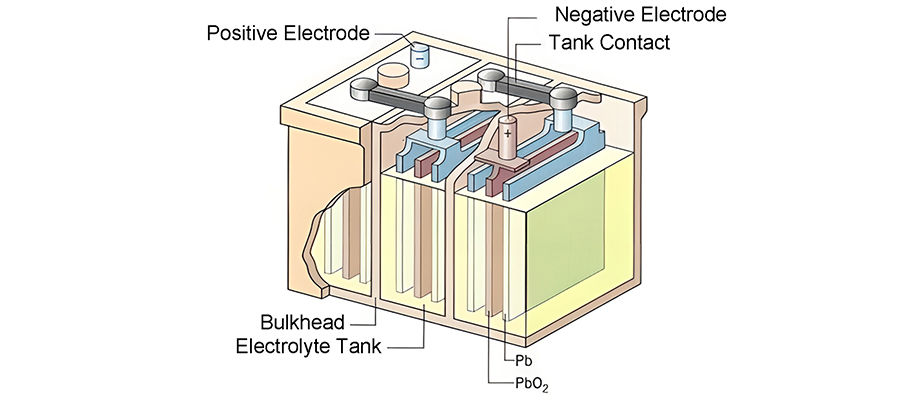
(2) Advantages
- Technology is very mature, simple structure, low cost, easy maintenance; -Cycling life can be up to about 1000 times.
- Cycle life up to about 1000 times; -Efficiency up to 80% to 90%.
- Efficiency up to 80% to 90%, cost-effective.
(3) Disadvantages
- Decrease in usable capacity in deep, fast and high power discharge; -Lower energy density, lower life time.
- Lower energy density, shorter life.
- Lead metal has a greater impact on the environment
(4) Application
Lead-acid batteries are often used as accidental or backup power for power systems, and in the past, most stand-alone photovoltaic power generation systems were equipped with such batteries. Currently there is a trend to gradually be replaced by other batteries (such as lithium-ion batteries).
3.2 Lithium-ion Battery
(1) Basic Principle
Lithium-ion battery is actually a lithium-ion concentration battery, positive and negative electrodes are composed of two different lithium ion embedded compounds.
When charging, Li + from the positive electrode de-embedded through the electrolyte embedded in the negative electrode, the negative electrode is in the lithium-rich state, the positive electrode is in the lithium-poor state.
Discharge is the opposite, Li + from the negative electrode de-embedded, through the electrolyte embedded in the positive electrode, the positive electrode in the lithium-rich state, the negative electrode in the lithium-poor state.
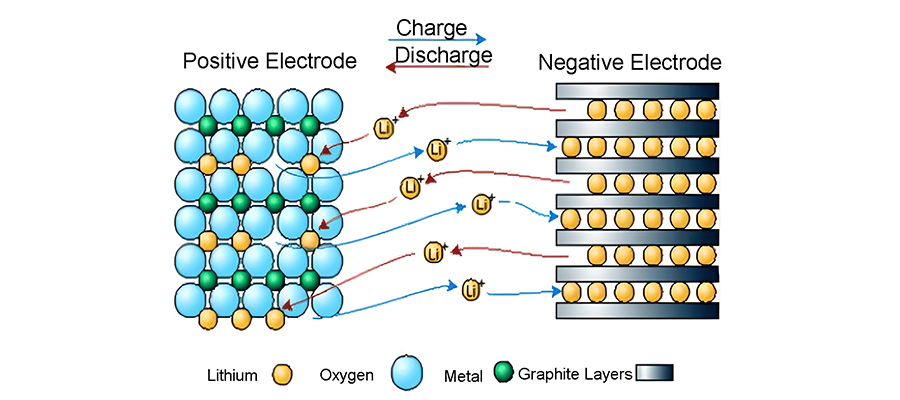
(2) Advantages
- Lithium-ion battery efficiency can reach more than 95%.
- Discharge time can be up to several hours.
- Cycling up to 5000 times or more, fast response.
Lithium-ion batteries are practical batteries with the highest specific energy in batteries. And there are a variety of materials that can be used for its anode and cathode. For example: lithium cobaltate lithium-ion batteries, lithium manganate lithium-ion batteries, lithium iron phosphate lithium-ion batteries and so on.
(3) Disadvantages
- The price of lithium-ion batteries is still high.
- Sometimes overcharging can lead to heat, combustion and other safety issues.
(4) Application
Because of the application of lithium-ion batteries in portable and mobile devices such as electric cars, computers, cell phones, etc.. It has now become almost the most widely used battery in the world.
The high energy density and power density of lithium-ion batteries is the main reason why it has been able to gain wide application and attention. Its technology is developing rapidly, and in recent years, mass production and multi-occasion applications have led to a sharp decline in its price, and thus its increasing use in power systems.
Lithium-ion battery technology is still under continuous development, and current research is focused on further improving its service life and safety, cost reduction, and the development of new positive and negative electrode materials.
In addition, there are flywheel energy storage, super capacitor energy storage, superconducting energy storage and other technologies, but the current application scale is small. The above three are the current mainstream large-scale power storage technology. With the development of technology, a variety of energy storage methods will continue to improve and application.


Very informative read! The breakdown of different electrical energy storage technologies is helpful for understanding the future of energy management. Great overview of the pros and cons of each option!