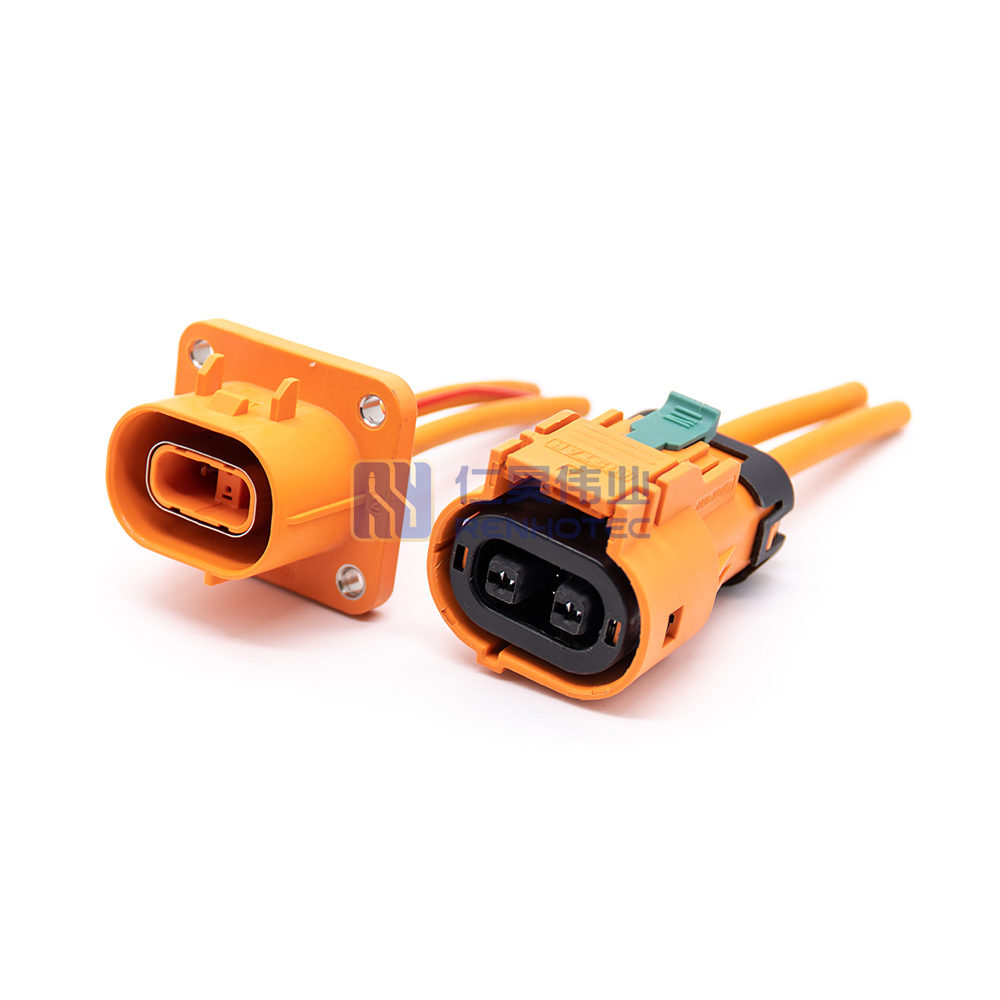
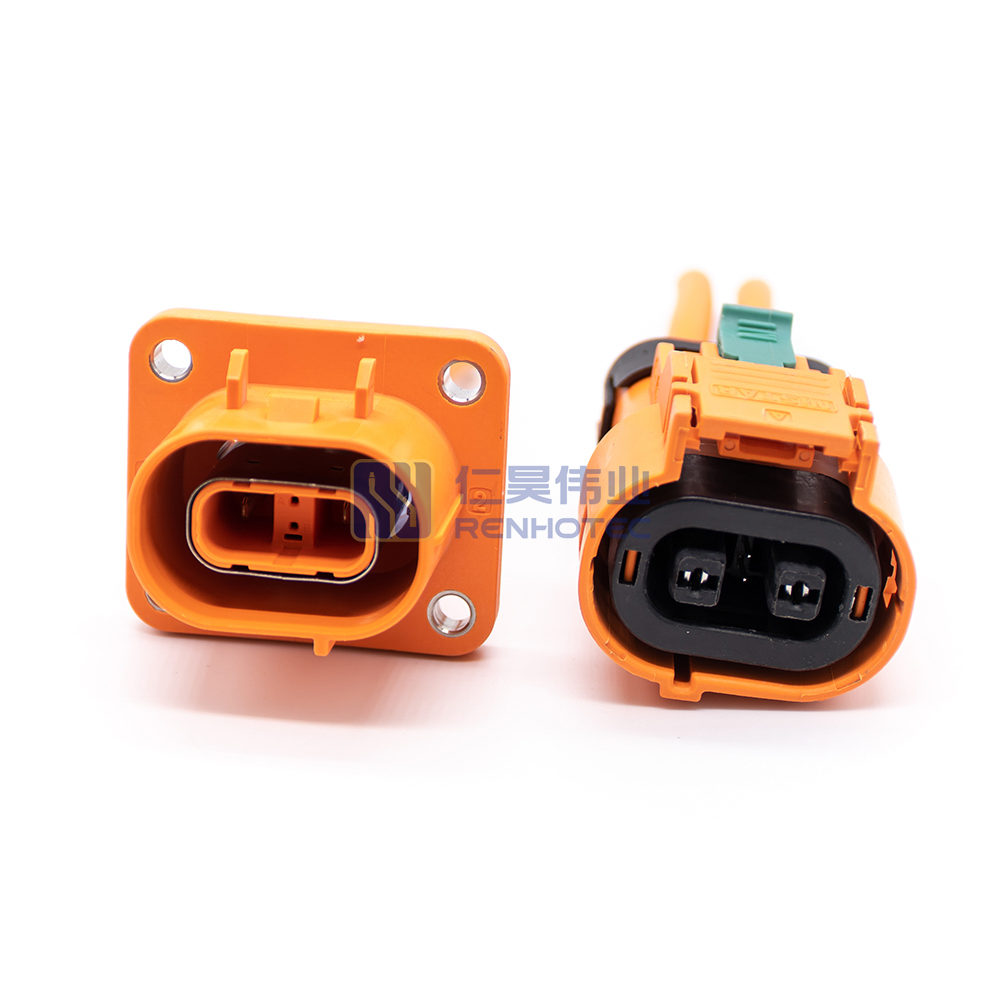
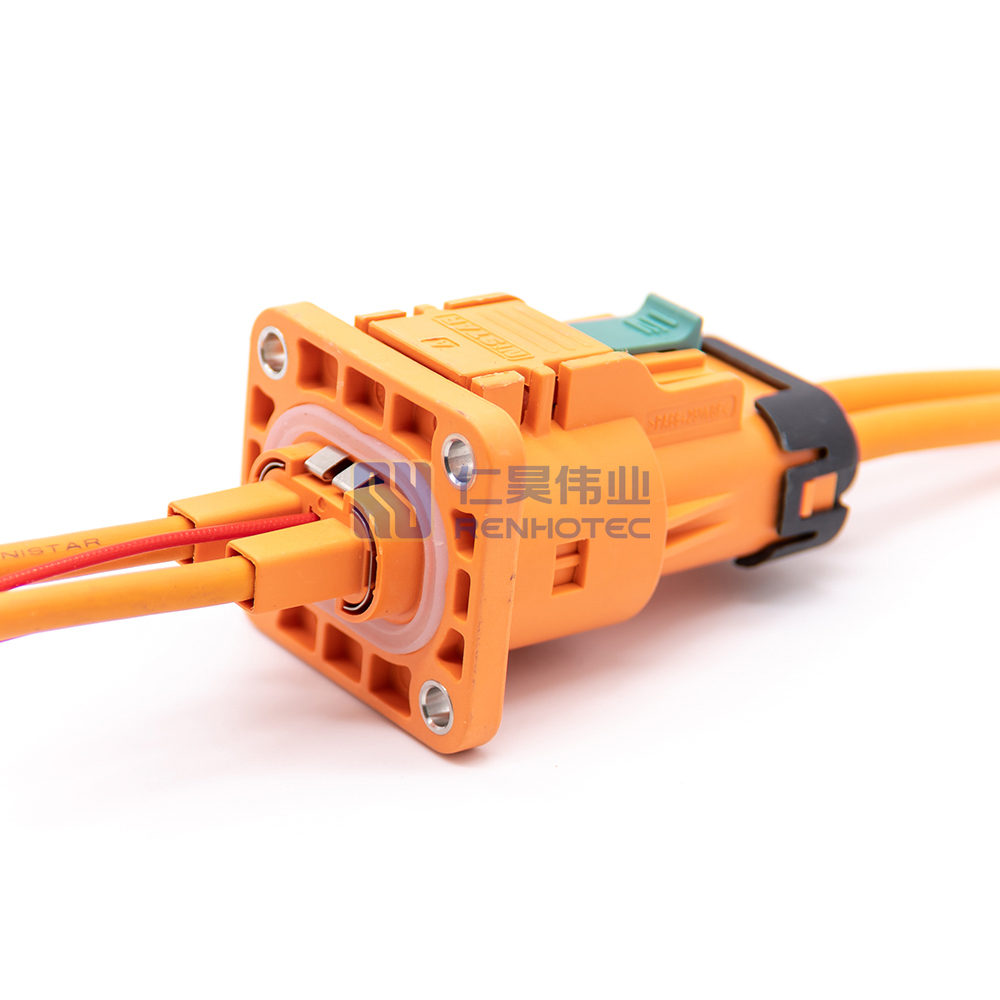
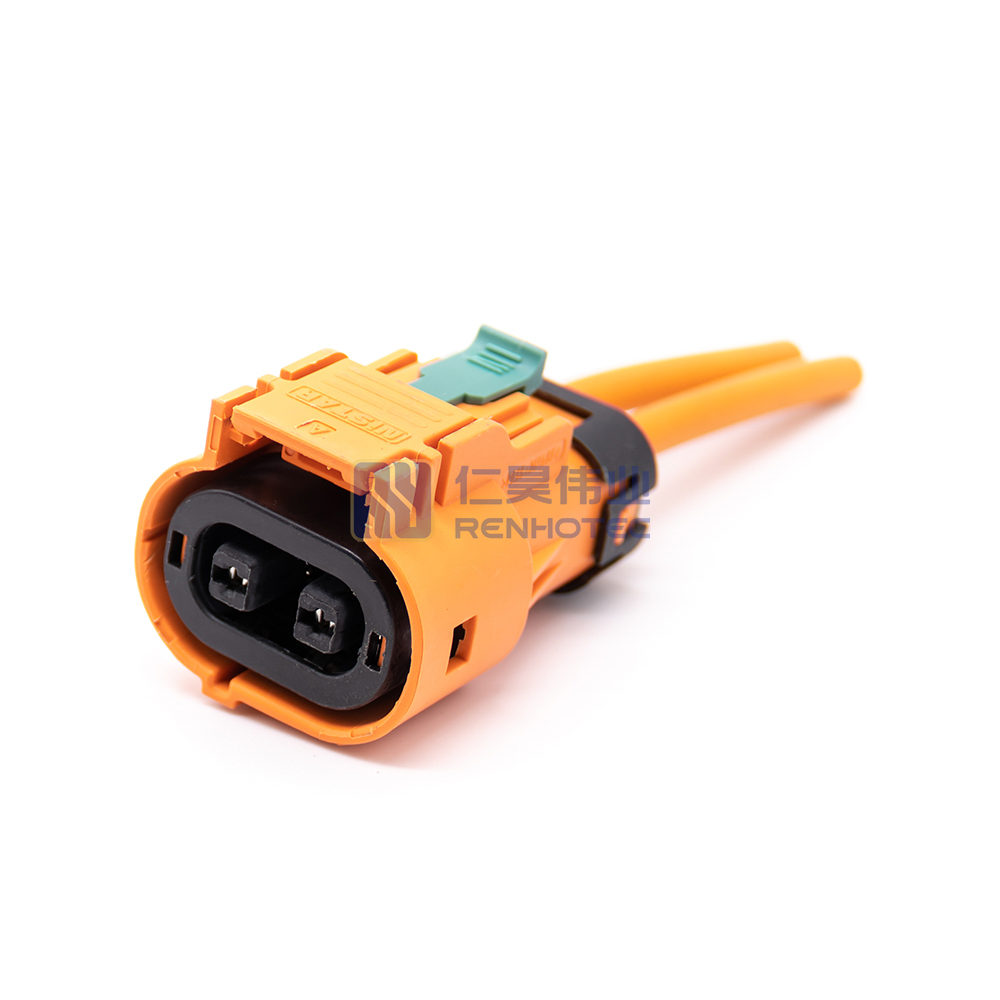
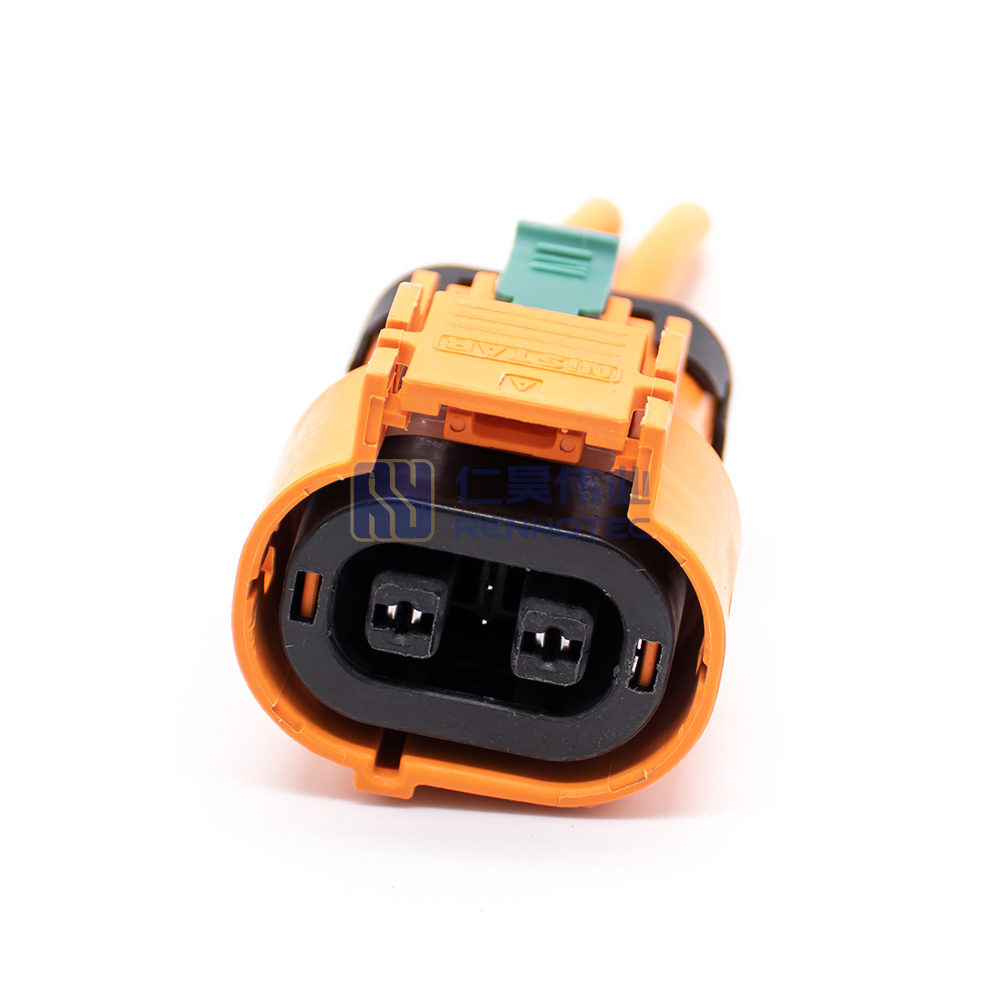
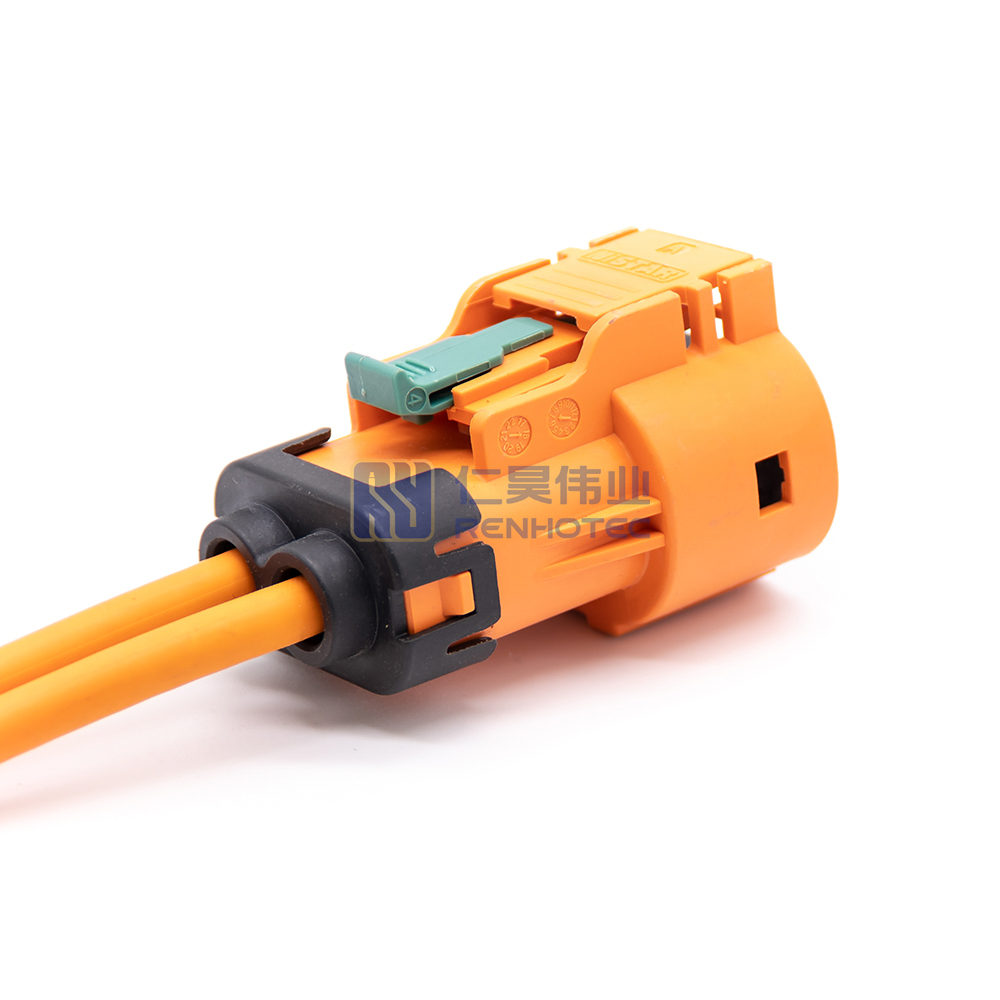
Product Type
| Connector Type | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Orientation | |||
| Number of Positions | |||
| Terminal | 2.8mm |
||
| Wire Gauge | 4mm² |
||
| Shell Material | PA66+GF |
||
| Mounting Type | Cable Mount |
||
| Key | A |
||
| Connector Type | Orientation | ||
| Number of Positions | Terminal | 2.8mm |
|
| Wire Gauge | 4mm² |
Shell Material | PA66+GF |
| Mounting Type | Cable Mount |
Key | A |
Environmental Characteristics
| Ingress Protection | IP67 |
|---|---|
| Ingress Protection | IP67 |
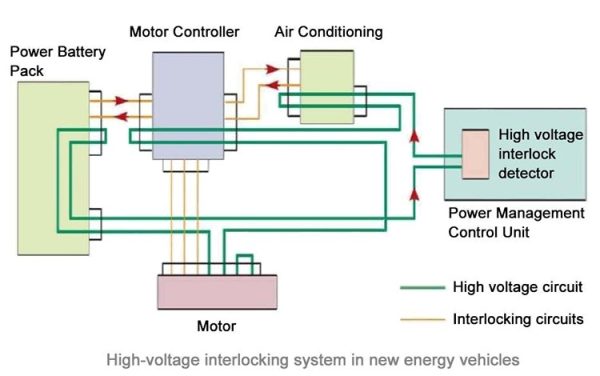
High-voltage interlock (hvil for short), a safe design method that uses low-voltage signals to manage high-voltage circuits. In the high-voltage system design, in order to avoid the arcing caused by the high-voltage connector being opened and closed during the actual operation. The high-voltage connector should generally have the “high-voltage interlock” function.
Connectors with high-voltage interlocks are unlocked when energized. It can be disconnected by a logical sequence of high-voltage interlocks. The disconnection time is related to the difference in the effective contact length between the high-voltage interlock terminal and the power supply terminal. It is related to the speed when disconnected.
Under normal circumstances, the response time of the system to the interlock terminal circuit is between 10 and 100ms. When the disconnection (unplugging) time of the connected system is less than the system response time. There will be a safety risk of live plugging and unplugging. And the second unlocking is in order to solve this disconnection time problem. Under normal circumstances, the secondary unlocking can effectively control the disconnection time above 1s to ensure safe operation.
High voltage interlocks for high voltage electrical circuits such as high voltage connectors, msds and high voltage distribution boxes are commonly available.