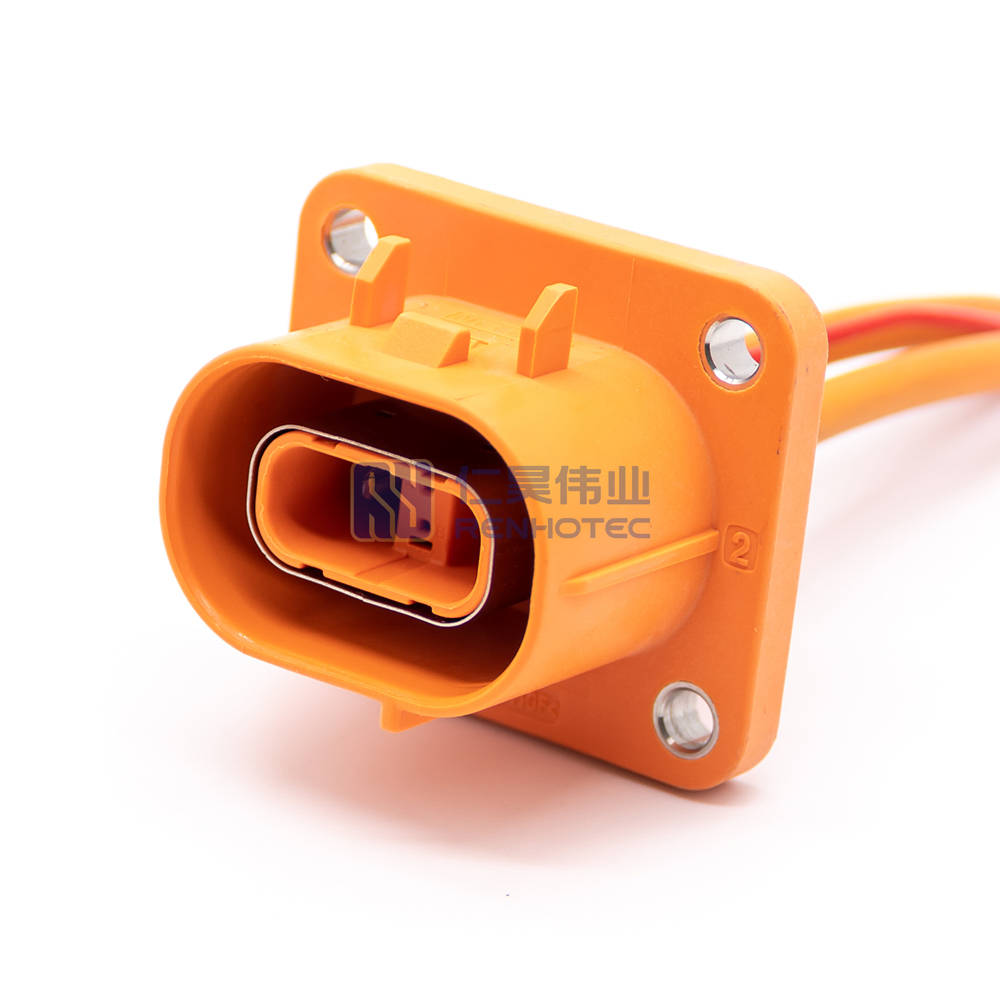
High-voltage connectors can be distinguished in a variety of ways, and will vary from industry to industry. This article is only for the new energy automotive high-voltage connectors to do the elaboration. Connectors are divided into many types according to the different use of location and requirements.
1.Classification of High-voltage Connectors
(1) According to the type of terminal points
Square terminal structure. The use of stamping terminal technology, the lower cost of this category of terminals, mold requirements and mold costs are high, the application of small currents below 40A more widely.
Round terminal structure. The use of machined terminal technology is the main, terminal cost relative to the stamping terminal, the cost is higher. However, due to the use of machined production methods, no or very low mold input, the terminal pre-investment is less.
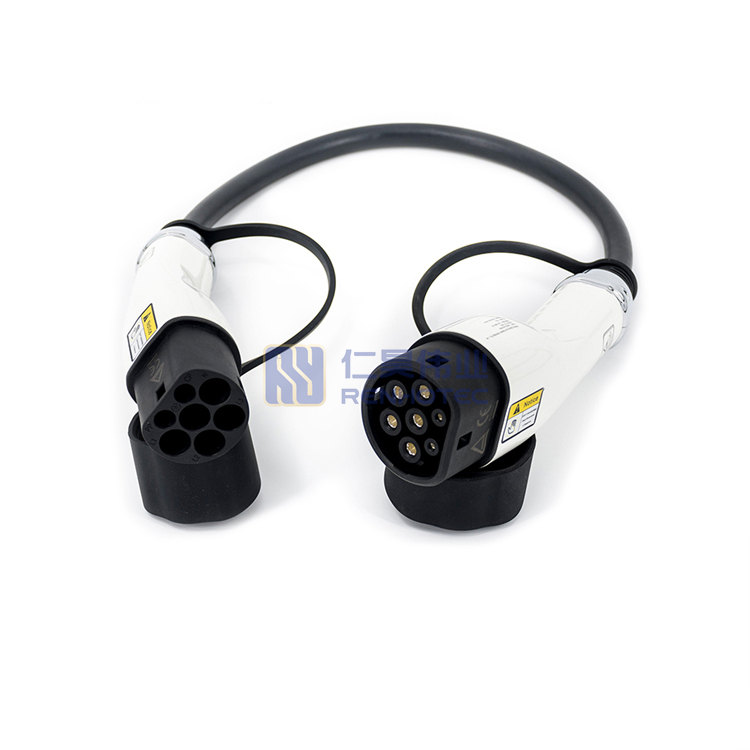
More representative products are TEHVA800 series, domestic mainstream product series.
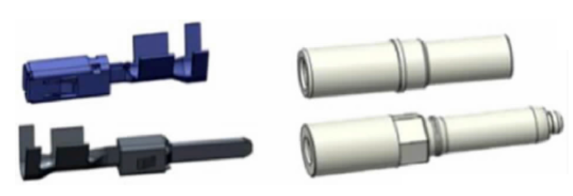
(2) According to the type of structure points
Connector structure according to the installation method can be divided into plugs, sockets. Plug can be divided into linear plug, 90°right angle plug. Sockets can be divided into flange socket, 90°right angle socket, linear socket, etc.
(3) Classified according to the current used
Low-voltage small-current connectors: voltage 24V DC, current less than 1A. e.g. TO series connectors.
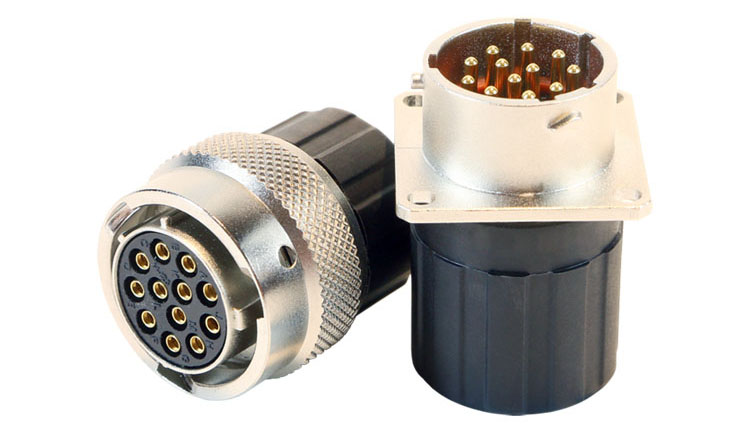

High voltage low current connectors: voltage 500-800V DC/AC, current 50A or less. e.g. PL60 two-pole series connector.
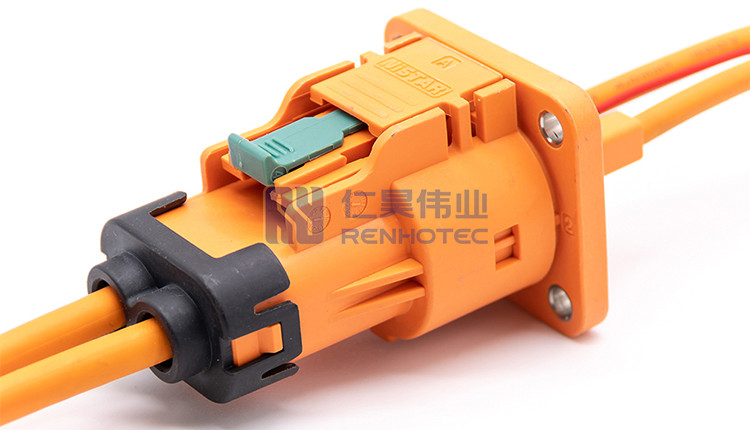

High voltage high current connectors: voltage 500-800V DC/AC, current 50A-500A. e.g. PL300 single pole.
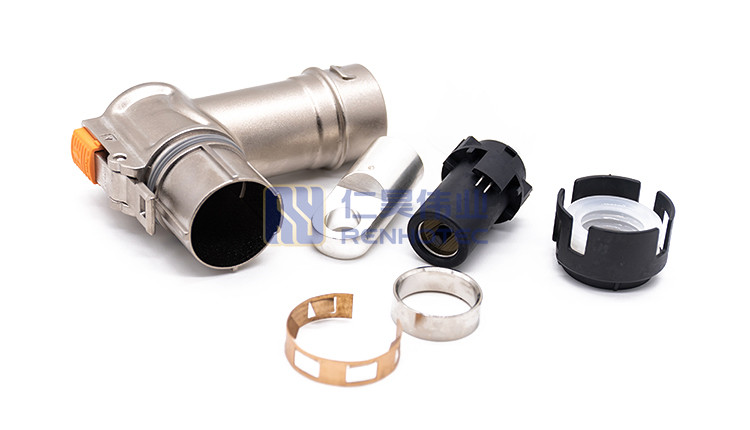

(4) Classification of high voltage and high current connectors
There are mainly MSD connectors, HV push-pull connectors, battery junction boxes, PL connectors, HVM connectors, charging stand and charging head, and some other custom connectors.

(5) According to the size of the product current, it can be roughly divided into three types of application intervals
A 16-50A are mostly two-core and three-core high-voltage and low-current connectors. It is usually used in high-voltage power distribution boxes (DC+/-, electric defrosting, fans, air conditioners, PTC, etc.), and power supply connections for small power devices around the electric control.
B 80-125A are usually single-core, two-core, and three-core high-voltage and high-current connectors. Usually used in high voltage distribution box, motor controller, battery box, DC charging stand to battery connection.
C 150-500A are usually single-core, two-core, and three-core high-voltage and high-current connectors. Applied to high-voltage power distribution box (battery +/-, motor +/-), motor controller UVW three-phase interface, battery box +/- pole, DC charging stand to battery connection.
(6) Data connectors and high-voltage connectors
Connectors are divided into data connectors and high-voltage connectors 2 major categories. High-voltage connector board inside a low-voltage connector board. This low-voltage connector compared to the data connector, then, the voltage is still much higher, just not as high voltage connector can carry 1000V DC.

(7) High-voltage connectors according to the surface material classification
Divided into plastic high-voltage connectors and metal high-voltage connectors
Plastic high-voltage connectors: usually single-core, two-core, and three-core, current-carrying capacity of 10-500A.

Metal high-voltage connectors: usually single-core, two-core, current-carrying capacity of 10-500A.

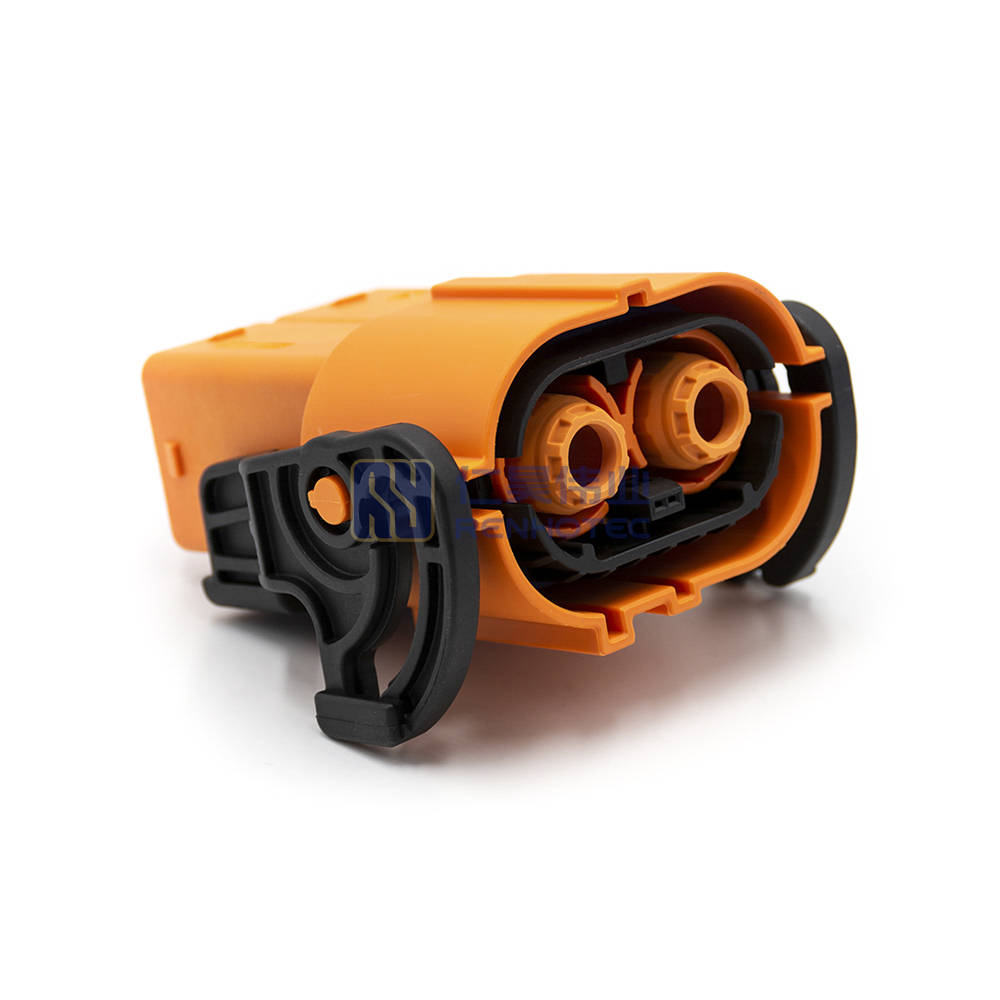
(8) Unshielded connector and shielded connector
High-voltage connectors are divided into unshielded connector and shielded connector according to the function of shielding or not. The internal structure of non-shielded connectors is relatively simple, without shielding function, the cost is relatively low, also save the installation cost of shielding function.
It can be applied on the parts that do not need shielding function. Such as charging circuit, inside the controller, inside the battery pack shell and inside the control, etc. on the appliances covered by metal shell.
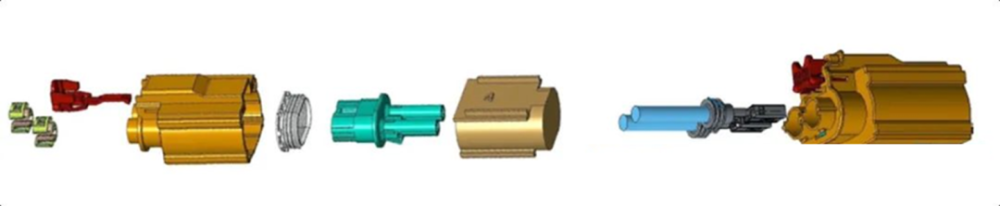
Shielded connectors are the opposite. Shielded connectors are complex in structure, have shielding requirements and are relatively costly. Suitable for places where shielding is required, suitable for application in the high-voltage harness connection. Such as the external part of the appliance and the high-voltage harness connection with the shielding function.

(9) According to the different ways of harness connection, there are two types of connection: fixed and plug-in type
One is the fixed type which is directly connected by bolts.
Bolt connection is a connection method often seen on the whole vehicle. The advantage of this method is the reliability of the connection. The mechanical force of the bolts is resistant to the effects of automotive grade vibration, and its cost is relatively low.
The inconvenience of course is that bolted connections require a certain amount of space to operate and install. It is not suitable from the point of view of batch operation and after-sales maintenance, and the more bolts there are, the greater the risk of human error, so it also has certain limitations.
Similar products were often seen in early Japanese and American hybrid models, and now many similar connections can be seen in the three-phase motor lines of some passenger cars and the battery power input and output lines of some commercial vehicles.
This type of connection generally requires the use of external boxes to achieve other functional requirements such as protection. So whether to use this way need from the perspective of the entire vehicle power line design layout combined with after-sales requirements to choose.

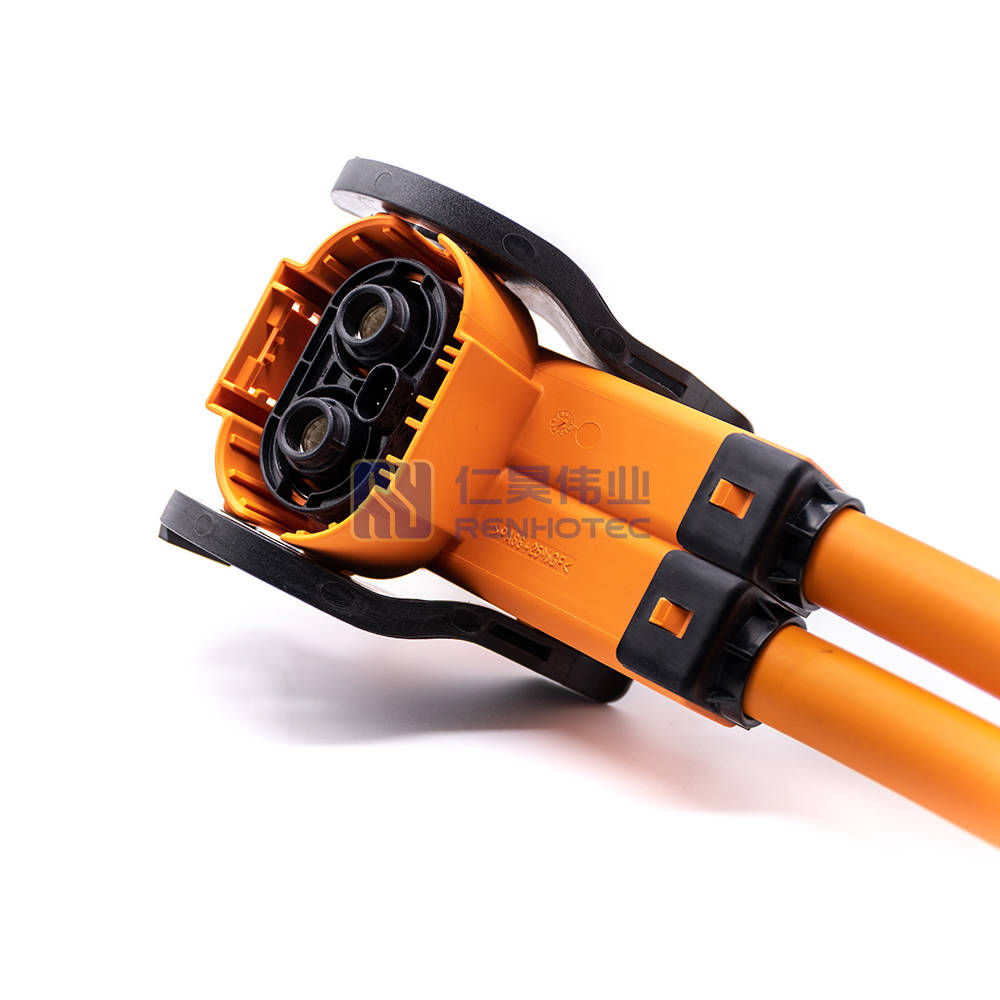
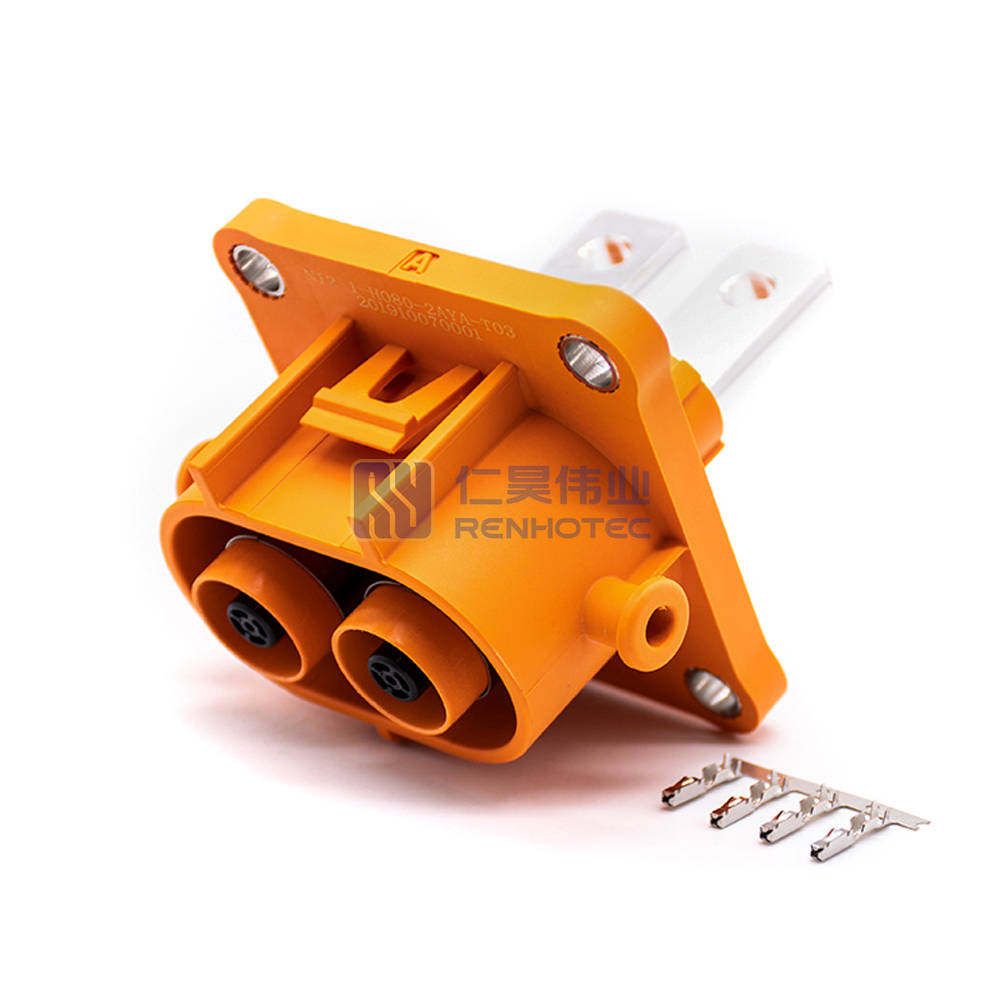
The most common high-voltage connector parts include the following: Female Connector, Male connector, Male connector contains two categories, Inline version and Header version. And then split to the lowest sub-part-Terminal: carrying power, usually fixed in the plastic shell, mainly divided into female terminal, male terminal, Busbar, etc..
2. The Development Process
The development of high-voltage connectors for electric vehicles is synchronized with the development of electric vehicles. From the connector point of view, the development of domestic high-voltage connectors through the following generations.
The first generation of high-voltage connector from the industrial connector adapted to the first generation. The second generation added the function of high-voltage interlock. The third generation of high-voltage connectors are characterized by plastic + shielding function + high-voltage interlocking.
Domestic electric vehicle connectors from metal shell to plastic shell, the application types are as follows:
(1) The first generation of high-voltage connector products to the metal shell mainly, does not have a high-voltage interlocking function, and anti-mis-insertion effect in general. The 2nd generation of high-voltage connectors in the 1st generation of high-voltage connectors based on the addition of high-voltage interlocking function, the connector shell material from metal to plastic.


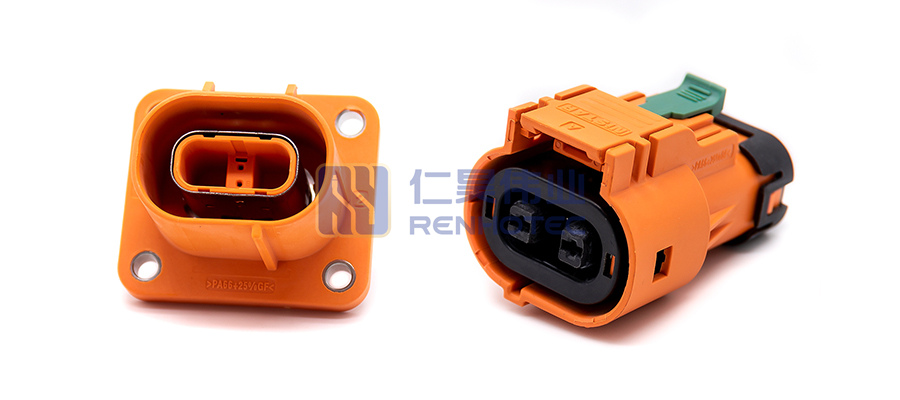
(2) The third generation of high-voltage connectors, that is, plastic + shielding function + high-voltage interlocking high-voltage connectors. This type of connector is representative of the industry’s 800 series products. It is through the operation sequence to achieve part of the secondary unlocking function, not a direct mechanical structure.

(3) Gradually the emergence of plastic + shielding function + high-voltage interlocking + secondary unlocking of the 4th generation of high-voltage connectors. The fourth-generation high-voltage connector has a special mechanical structure to achieve a secondary unlocking function, greatly improving the safety factor. Representative of the industry is the 280 series products, these products are through the mechanical structure to achieve the second unlocking function, more secure.

(4) Relative to the 4th generation of products, the future generation of high-voltage connectors to solve the problem is how to effectively improve the transmission energy density through cooling, reduce the quality and improve the overall performance of the product . Such as with high-power charging with liquid cooling, air-cooled way.
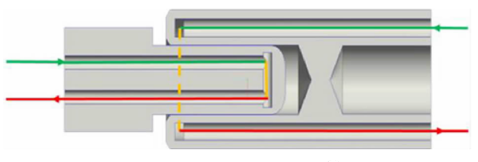
With the continuous development of the new energy vehicle market and technological innovation to promote the type of new energy high-voltage connectors and technology will also continue to innovate and improve. In the future, with the continuous progress of technology and application of expanding, new energy high-voltage connectors will be widely used in more areas.





