"As the core component of the high-voltage wiring harness of new energy vehicles, the correct selection of high-voltage cable is very critical. Generally, some important information is mainly referred to: customer standards, actual applications and special requirements, so as to select safe and appropriate high-voltage cables."
1.Cable Size Selection
1.1 Factors to Consider in High-Voltage Cable Size Selection
The cable size selection mainly refer to the following factors:
- conductor design standards, such as LV216-1/2, ISO19642 and other;
- conductor working voltage platforms and voltage ranges;
- effective working current of the loop;
- working environment temperature of high-voltage conductors;
- circuit peak current and peak duration;
- circuit fuse capacity;
- and allowable crimping diameter of high-voltage harness plug-ins.
1.2 High-Voltage Cable Size Selection Steps
The basic steps for high-voltage conductor selection are as follows:
- Verify the working voltage platform of the high-voltage conductor. Currently, the general voltage platform is below 1000V DC, so high-voltage conductors with a resistance of 1000V DC are often used;
- Select the conductor diameter based on the temperature rise curve combining the conductor current carrying capacity and the working environment temperature;
- Compare the peak current, peak duration and conductor smoke curve (see Figure 1), and the peak duration is less than the conductor smoke time;
- Compare the fuse blowing time and the conductor smoke time, and the conductor smoke time is greater than the fuse blowing time;
- After the above steps, preliminarily determine the conductor diameter, and then combine the high-voltage plug-in model and specification to confirm whether the conductor can be used, especially the need to verify that the high-voltage plug-ins on both sides of the conductor need to meet their requirements at the same time.
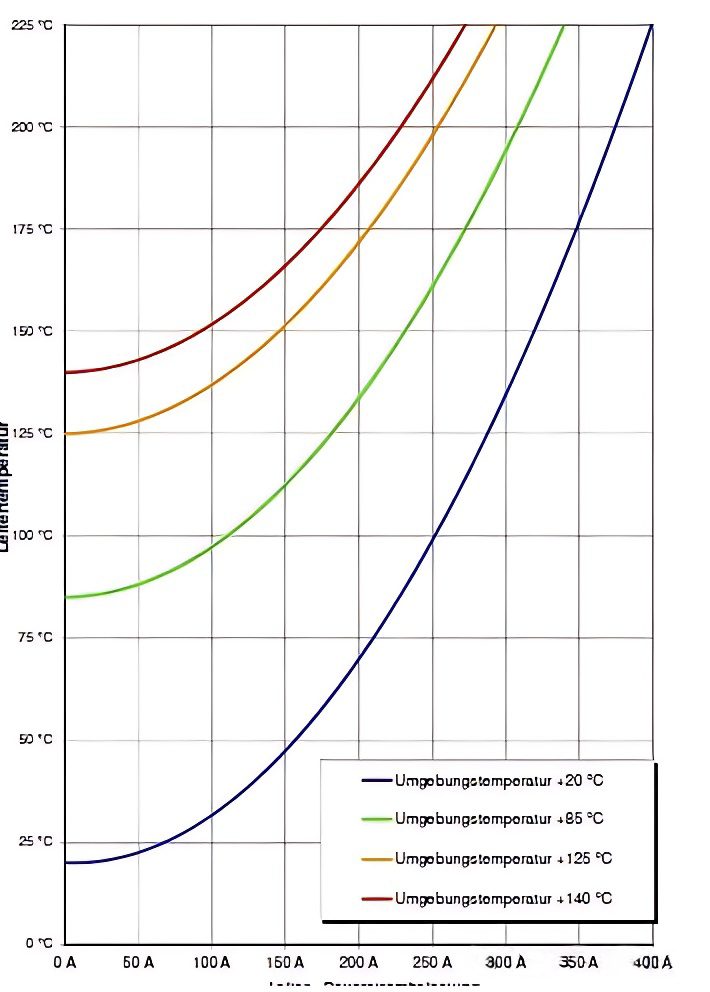
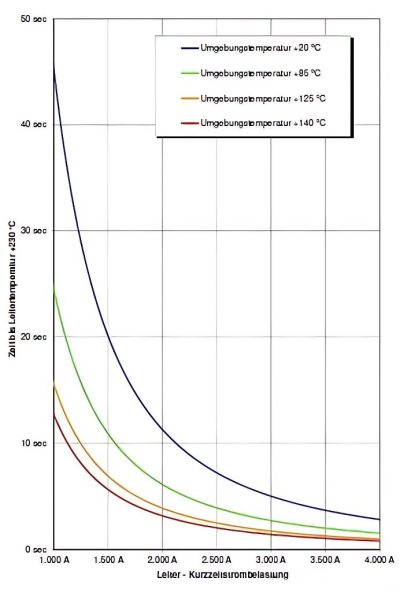
2.Jacket Material Selection
2.1 Silicone Cable
Silicone cable is soft and has good temperature resistance, but poor tear and oil resistance. Silicone cable is recommended in the following environments:
- Areas where the working environment temperature is greater than 150°C;
- Areas where the wiring harness layout space is small and the complete radius does not meet 5D, or areas where the softness of the wiring harness is strictly required due to assembly requirements.
- Areas with better protection of high-voltage harnesses, no oil and no wear;
- Areas with clear use requirements for high-voltage plug-ins.
2.2 Cross-linked Polyolefin(XLPO) Cable
Cross-linked polyolefin(XLPO) cable is harder in material, has good wear and tear resistance, and is of low cost, but has poor softness and temperature resistance. It needs to be used in the following environment:
- The working environment temperature is not greater than 150°C;
- The wiring harness layout space is large, the complete radius≥5D, or there is no difficulty in wiring harness assembly;
- The wiring harness may come into contact with oil, or the wear and vibration amplitude is large;
- and there are clear usage requirements for high-voltage plug-ins.
3.Other Cables
If there is a flame retardant requirement for the cable, you can choose HB or V0 grade cable; if there is or isn’t requirements for shielding, you can choose unshielded cable, single-layer shielded cable, double-layer shielded cable, and the shielding density of the cable can be defined according to the shielding requirements. Generally, the shielding density is above 85%.
Related Products
-
1500V 100A High Voltage Unshielded EV Cable 16mm2 Energy Storage System Cable
-
1500V 125A High Voltage Shielded Cable 25mm2 Energy Storage System Cable
-
1500V 125A High Voltage Unshielded EV Cable 25mm2 Energy Storage System Cable
-
1500V 165A High Voltage Shielded Cable 35mm2 Energy Storage System Cable



